Cloud-native architecture
Real-time analytics requires a scalable, high-performance, and cost-efficient database that can handle high-ingest rates and low-latency queries without overprovisioning. is designed for elasticity, enabling independent scaling of storage and compute, workload isolation, and intelligent data tiering.Independent storage and compute scaling
Real-time applications generate continuous data streams while requiring instant querying of both fresh and historical data. Traditional databases force users to pre-provision fixed storage, leading to unnecessary costs or unexpected limits. eliminates this constraint by dynamically scaling storage based on actual usage:- Storage expands and contracts automatically as data is added or deleted, avoiding manual intervention.
- Usage-based billing ensures costs align with actual storage consumption, eliminating large upfront allocations.
- Compute can be scaled independently to optimize query execution, ensuring fast analytics across both recent and historical data.
Workload isolation for real-time performance
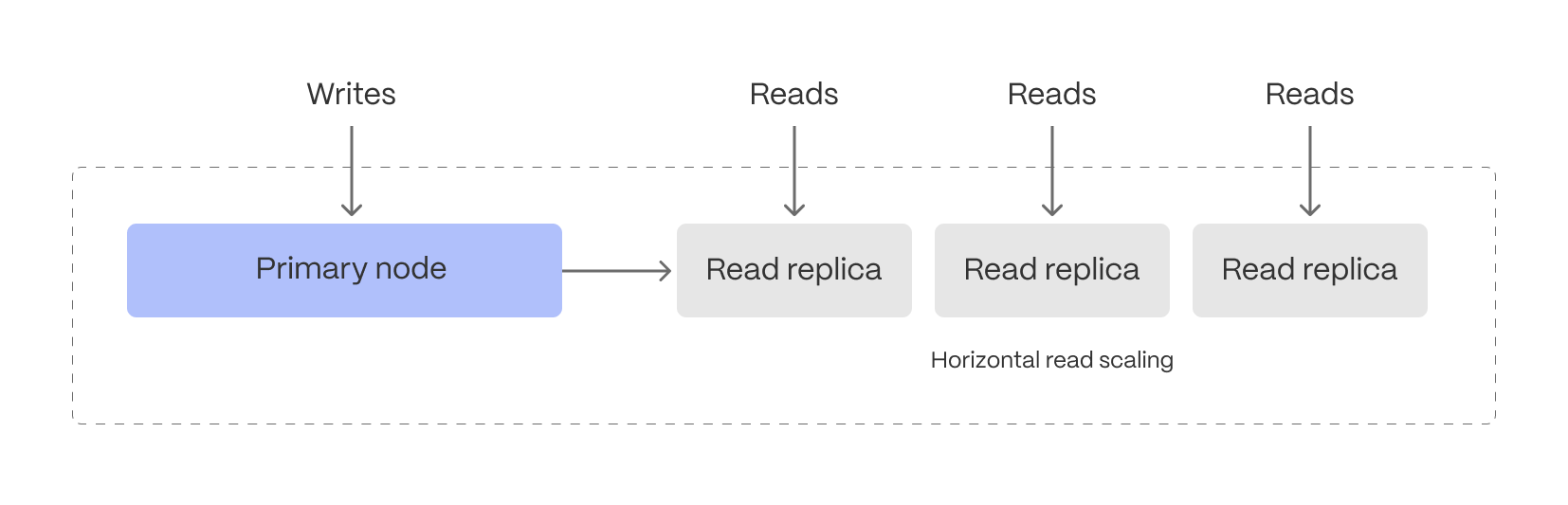
Balancing high-ingest rates and low-latency analytical queries on the same system can create contention, slowing down performance. mitigates this by allowing read and write workloads to scale independently:- The primary database efficiently handles both ingestion and real-time rollups without disruption.
-
Read replicas scale query performance separately, ensuring fast analytics even under heavy workloads.
Intelligent data tiering for cost-efficient real-time analytics
Not all real-time data is equally valuable—recent data is queried constantly, while older data is accessed less frequently. can be configured to automatically tier data to cheaper bottomless object storage, ensuring that hot data remains instantly accessible, while historical data is still available.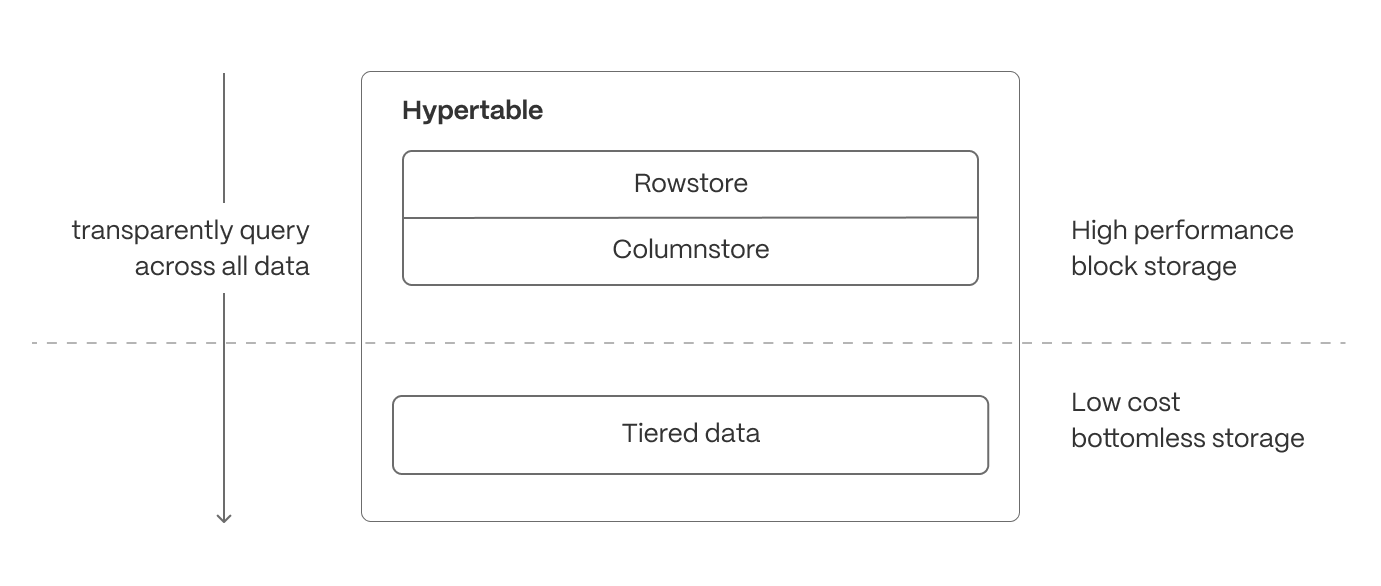
- Recent, high-velocity data stays in high-performance storage for ultra-fast queries.
- Older, less frequently accessed data is automatically moved to cost-efficient object storage but remains queryable and available for building continuous aggregates.
Cloud-native database observability
Real-time analytics doesn’t just require fast queries—it requires the ability to understand why queries are fast or slow, where resources are being used, and how performance changes over time. That’s why is built with deep observability features, giving developers and operators full visibility into their database workloads. At the core of this observability is Insights, ’s built-in query monitoring tool. Insights captures per-query statistics from our whole fleet in real time, showing you exactly how your database is behaving under load. It tracks key metrics like execution time, planning time, number of rows read and returned, I/O usage, and buffer cache hit rates—not just for the database as a whole, but for each individual query. Insights lets you do the following:- Identify slow or resource-intensive queries instantly
- Spot long-term performance regressions or trends
- Understand query patterns and how they evolve over time
- See the impact of schema changes, indexes, or continuous aggregates on workload performance
- Monitor and compare different versions of the same query to optimize execution
Ensuring reliability and scalability
Maintaining high availability, efficient resource utilization, and data durability is essential for real-time applications. provides robust operational features to ensure seamless performance under varying workloads.- High-availability (HA) replicas: deploy multi-AZ HA replicas to provide fault tolerance and ensure minimal downtime. In the event of a primary node failure, replicas are automatically promoted to maintain service continuity.
- Connection pooling: optimize database connections by efficiently managing and reusing them, reducing overhead and improving performance for high-concurrency applications.
- Backup and recovery: leverage continuous backups, Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR), and automated snapshotting to protect against data loss. Restore data efficiently to minimize downtime in case of failures or accidental deletions.

