 s in are a kind of that is refreshed automatically
in the background as new data is added, or old data is modified. Changes to your
dataset are tracked, and the behind the is
automatically updated in the background.
s have a much lower maintenance burden than regular materialized
views, because the whole view is not created from scratch on each refresh. This
means that you can get on with working your data instead of maintaining your
database.
Because s are based on s, you can query them in exactly the same way as your other tables. This
includes s in the , compressed into the ,
or tiered to object storage. You can even create s on top of your s,
for an even more fine-tuned aggregation.
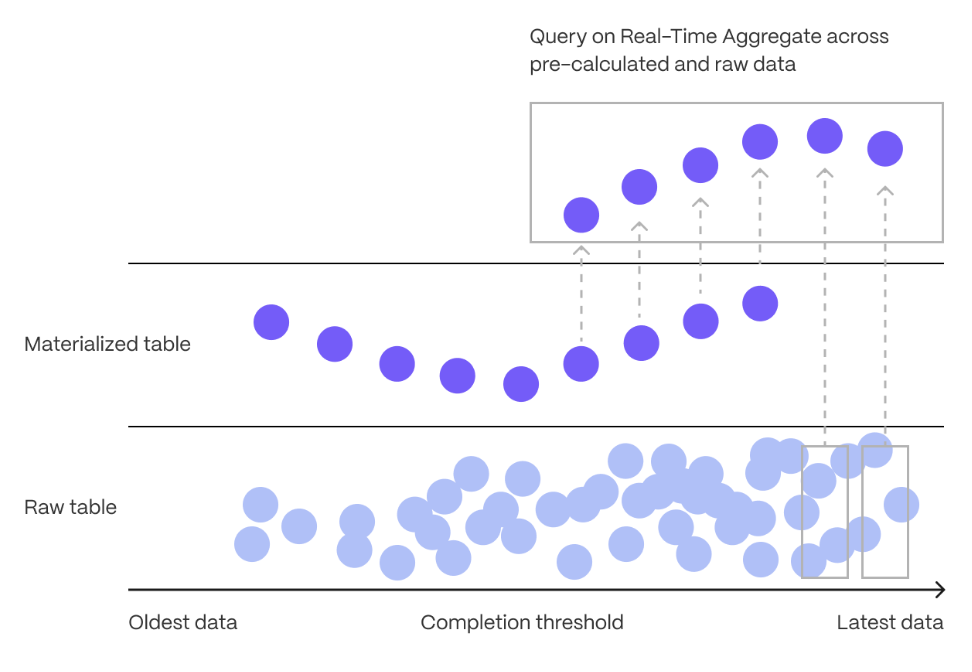
Real-time aggregation enables you to combine pre-aggregated data from the materialized view
with the most recent raw data. This gives you up-to-date results on every query.
For more information about using s, see the documentation in Use products.
s in are a kind of that is refreshed automatically
in the background as new data is added, or old data is modified. Changes to your
dataset are tracked, and the behind the is
automatically updated in the background.
s have a much lower maintenance burden than regular materialized
views, because the whole view is not created from scratch on each refresh. This
means that you can get on with working your data instead of maintaining your
database.
Because s are based on s, you can query them in exactly the same way as your other tables. This
includes s in the , compressed into the ,
or tiered to object storage. You can even create s on top of your s,
for an even more fine-tuned aggregation.
Real-time aggregation enables you to combine pre-aggregated data from the materialized view
with the most recent raw data. This gives you up-to-date results on every query.
For more information about using s, see the documentation in Use products.
Samples
Create a
Create a that calculates hourly average temperature:Add a refresh policy
Automatically refresh the to keep it up to date:Manually refresh a
Refresh a specific time range in the :Query a
Query the just like a regular table:Available functions
Create and modify s
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW (Continuous Aggregate): create a on a or anotherALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW (Continuous Aggregate): change an existingDROP MATERIALIZED VIEW (Continuous Aggregate): drop a viewcagg_migrate(): migrate a from the old format to the new format introduced in 2.7
Refresh s
refresh_continuous_aggregate(): manually refresh a
Manage policies
add_continuous_aggregate_policy(): add policy to schedule automatic refresh of a
remove_continuous_aggregate_policy(): remove a refresh policy from a
Experimental policy management
add_policies(): add refresh, compression, and data retention policies on aalter_policies(): alter refresh, compression, or data retention policies on aremove_policies(): remove refresh, compression, or data retention policies from aremove_all_policies(): remove all policies from ashow_policies(): show all policies that are currently set on a

